¶ Calibration Guidelines
Calibrating a 3D printer offers numerous benefits:
Enhanced Printing Precision: Calibration ensures the accurate alignment of the printer’s axes and components, thereby improving printing precision and producing finer, more accurate models.
Improved Print Quality: By calibrating, issues such as layer shifting and detail loss due to printer inaccuracies can be avoided, leading to smoother surfaces and clearer details in printed models, thereby enhancing print quality.
Material and Time Savings: Calibration reduces wastage of materials and time caused by printing errors such as misalignment or failures, thus enhancing printing efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Extended Printer Lifespan: Regular calibration ensures that the printer’s components are in optimal condition, reducing wear and tear due to accumulated errors and extending the printer’s lifespan.
Reduced Maintenance Needs: Regular calibration minimizes the need for maintenance due to printer misalignment, thus reducing maintenance costs and time.
Overall, regular calibration is a crucial step in ensuring the proper functioning and print quality of a 3D printer, leading to improved efficiency, quality, and reliability while saving costs and time.
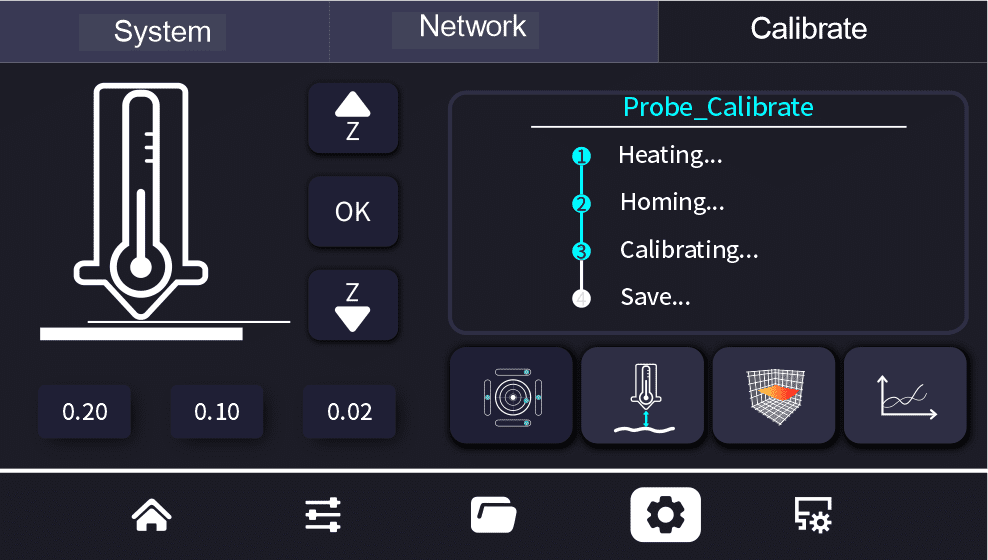
¶ Z-axis Offset Calibration
3D Printer Z-Axis Offset Calibration Steps
Purpose:
Calibrating the Z-axis offset is crucial for adjusting the distance between the nozzle and the print bed, which directly affects the quality of the first layer print.
1: Inspect the Nozzle and Print Bed
- First, inspect the printer’s nozzle and print bed to ensure both surfaces are clean, without any plastic residue or debris.
2: Prepare an A4 Paper
- With the nozzle and heated bed at room temperature, prepare an A4 paper for calibration.
3: Initiate Z-Axis Offset Calibration
- Click on the “Z-Axis Offset Calibration” option on the screen to prepare for calibration.
4: Perform Calibration
- Place the A4 paper between the nozzle and the print bed.
- Move the print bed up and down to adjust the Z-axis height.
- Stop when there is a slight friction resistance felt between the paper and the nozzle as well as the print bed.
5: Determine and Record the Z-Axis Offset Value
- Accept the current Z-axis height value; this value is the calibrated Z-axis offset obtained through calibration.
6: Apply the Calibration Value
- Apply the obtained Z-axis offset value to the printer settings to ensure the precision of the first layer print.
By following these steps, you can ensure that your 3D printer’s Z-axis is accurately calibrated, leading to improved print quality and adhesion for the first layer of your prints.
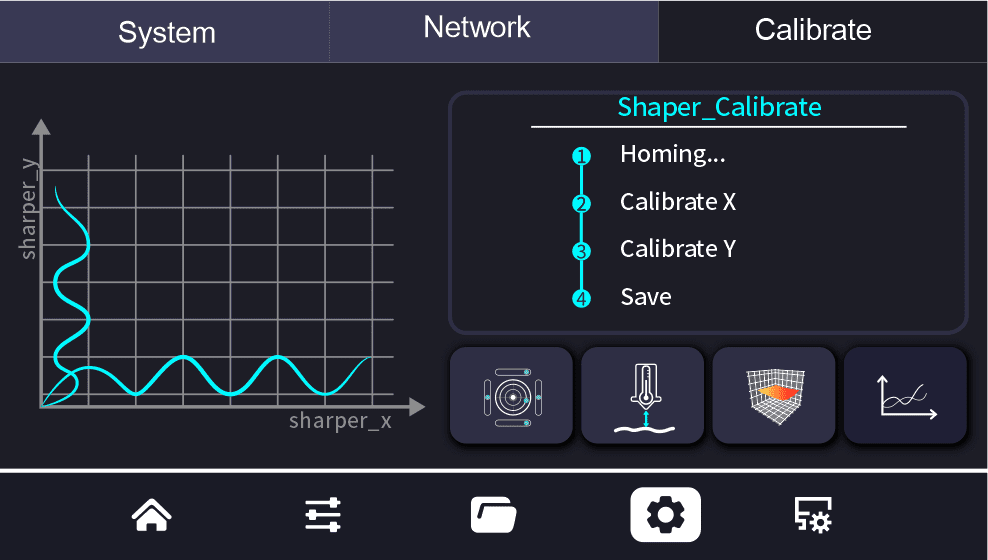
¶ Resonance Compensation Calibration
Introduction to Resonance Compensation Calibration Technology
Purpose:
Resonance compensation calibration is an advanced technique designed to reduce print artifacts known as z-bands or wobbles on 3D printed objects by adjusting the print parameters of the 3D printer. This technique significantly mitigates vibrations and resonance effects caused by the printer’s structural resonance, which is crucial for enhancing print quality.
Calibration Process:
- Resonance compensation calibration typically involves measuring the printer’s vibration response at various frequencies.
- Based on the measurement results, fine-tuning of the print parameters is performed to effectively counteract vibrations.
Benefits:
- By neutralizing vibrations, resonance compensation calibration can improve print accuracy, resulting in more precise and delicate models.
- With resonance effectively dampened, the printer can operate at higher speeds, as it is no longer constrained by the effects of vibration and resonance.
Further Optimization:
- Resonance compensation calibration is not only about addressing resonance issues; it also requires fine-tuning of other print parameters.
- Such fine-tuning helps optimize other aspects of the printing process, thereby enhancing overall print efficiency and quality.
This calibration process can be complex and may require specialized software and a good understanding of the printer’s dynamics. It’s often an iterative process that involves testing and adjusting until the desired results are achieved. Some 3D printers come with built-in auto-calibration features that simplify this process, while others may require manual calibration by the user.
¶ Bed Mesh Compensation Calibration
Function and Purpose:
Bed mesh compensation calibration is a technique used to optimize print quality by compensating for irregularities on the print bed, ensuring the uniformity of the first layer print. This technology is mainly used to address issues such as poor adhesion or warping caused by height differences between the nozzle and different areas of the heated bed.
Background of the Problem:
Under standard printing conditions, height differences in different areas of the heated bed can lead to adhesion problems or warping on the print bed, affecting the overall quality of the printed object.
Calibration Process:
- Mesh compensation calibration involves meticulously measuring the actual distance between the nozzle and different areas of the heated bed.
- Based on the measurement results, precise adjustments are made to the Z-axis offset values to achieve a uniform distribution across the heated bed surface.
Benefits:
- Mesh compensation calibration can significantly improve the adhesion and flatness of the printed bottom layer.
- This calibration ensures the consistency of the bottom layer print quality, thereby directly enhancing the quality of the entire printed object.
Efficiency Improvement:
- Implementing mesh compensation calibration can reduce material and time wasted due to printing failures.
- It helps users save costs and improve work efficiency by increasing the success rate of prints.
Conclusion:
Bed mesh compensation calibration is an essential step in improving 3D print quality, especially for users who pursue high precision and professional-level print quality, this technology is indispensable.
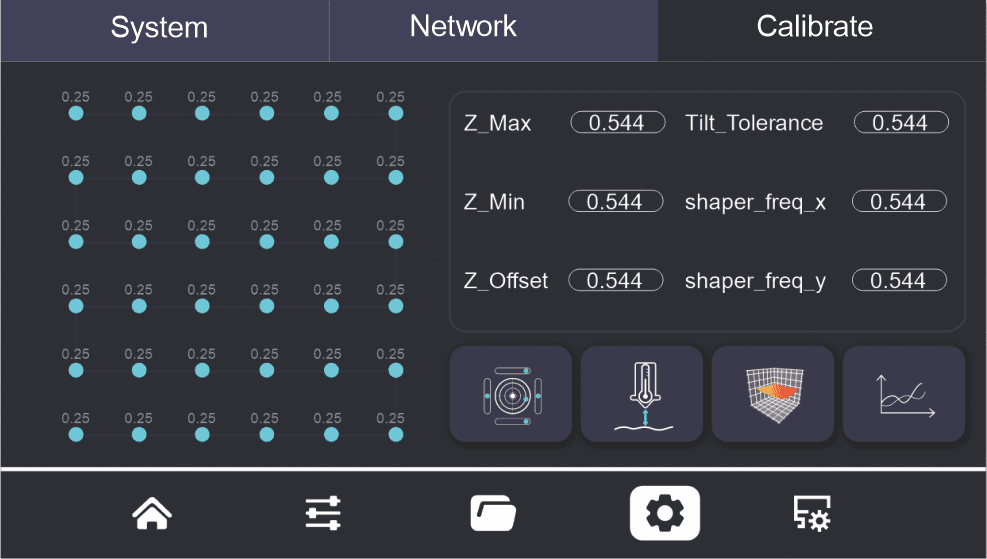
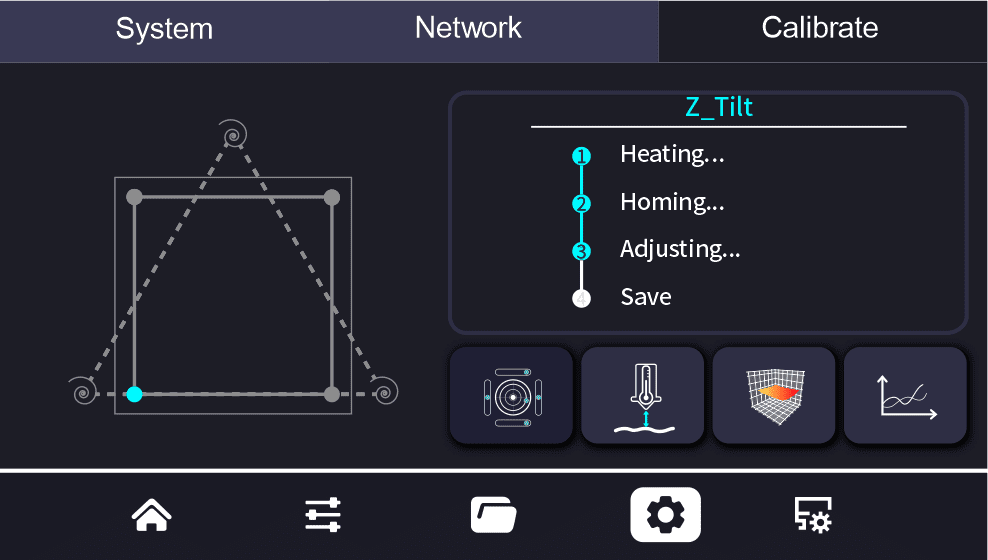
¶ Heated Bed Parallel Calibration
Heated Bed Parallel Calibration Technical Guide
Purpose:
Heated bed parallel calibration is an essential adjustment method aimed at ensuring that the heated bed is strictly parallel to the movement plane of the print head. This calibration is crucial for ensuring print quality and the long-term stable operation of the equipment.
Importance:
- If the heated bed is not parallel with the print head, it may lead to inconsistent bottom thickness of the printed object, affecting the overall quality and accuracy of the print.
- A heated bed that has not been calibrated over a long period can also cause instability during printing, and may even lead to premature wear or damage to the printer components.
Calibration Outcomes:
- Through heated bed parallel calibration, any tilt issues of the heated bed on the horizontal plane can be resolved, ensuring the uniformity of the printed object’s bottom.
- A calibrated heated bed contributes to increased stability during the printing process, thereby enhancing print quality and success rates.
Long-Term Benefits:
- Regularly performing heated bed parallel calibration not only helps maintain print quality but also reduces maintenance costs due to equipment failure.
- Calibration can extend the printer’s lifespan, reduce component wear, and thus improve the user experience and satisfaction.
Conclusion:
Heated bed parallel calibration is an indispensable part of 3D printing maintenance. By performing this simple calibration task, users can ensure print quality while also protecting the printer to ensure its long-term stable operation.
¶ Temperature Calibration
If you find that the temperature fluctuation is too large during printing, which leads to poor printing results, you can perform temperature calibration steps:
- Enter the machine’s IP in the web interface to access the fluidd page. Enter the following command in the status bar and send it. After calibration, enter the SAVE_CONFIG command to save it.
Nozzle Calibration Command
PID_CALIBRATE HEATER=extruder TARGET=170 (Change the final 170 value to the melting temperature required by your printing material)
Heated Bed Calibration Command
PID_CALIBRATE HEATER=heater_bed TARGET=60 (The following 60 value can be changed to the target temperature limit you need up to 100)